Revenue Optimization
The ability to optimize price based on forecasted demand, price elasticity and competitive rates has incredible benefits, and many companies are rushing to develop their own Revenue Optimization capabilities.
The primary aim of Revenue Optimization is selling the right product to the right customer at the right time for the right price. The essence of this discipline is in understanding customers’ perception of product value and accurately aligning product prices, placement and availability with each customer segment while at the same time ensuring Customer retention.
Price Optimization: Understanding customers’ perception of product value and accurately aligning product prices, placement and availability with each customer segment. 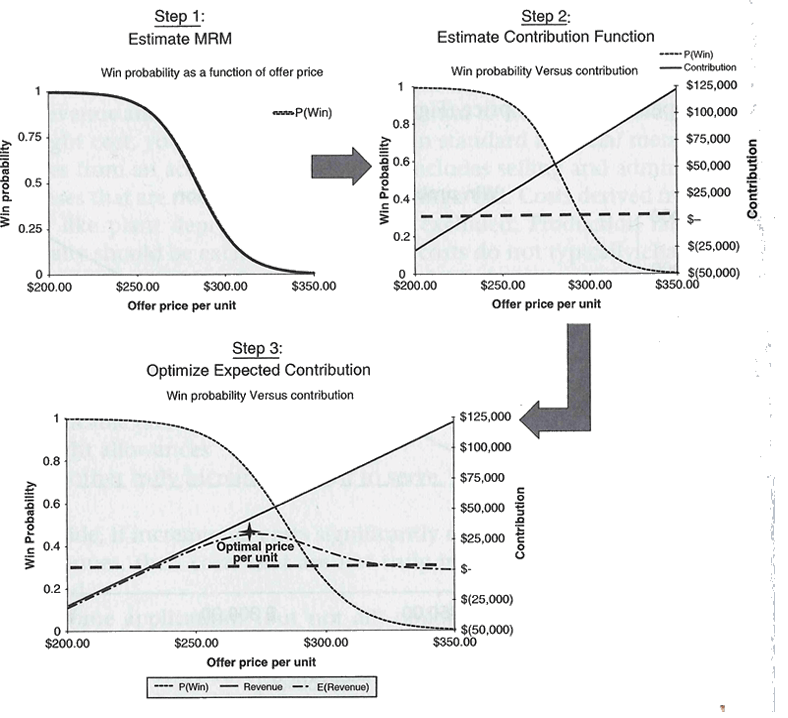
While forecasting suggests what customers are likely to do, optimization suggests how a firm should respond. Optimization is about evaluating multiple options on how to sell your product and to whom to sell your product. Optimization involves solving two important problems in order to achieve the highest possible revenue.
-
The first is determining which objective function to optimize. A business must decide between optimizing prices, total sales, contribution margins, or even customer lifetime values.
-
Secondly, the business must decide which optimization technique to utilize. For example, many firms utilize:
-
Linear programming, a complex technique for determining the best outcome from a set of linear relationships, to set prices in order to maximize revenue.
-
Regression analysis, involves finding the ideal relationship between several variables through complex models and analysis.
-
Discrete choice models can serve to predict customer behavior in order to target them with the right products for the right price.
-
Tools such as these allow a company the ability to optimize its product offerings, inventory levels, and pricing points in order to achieve the highest revenue possible while at the same time minimizing Customer churn.

